PLM & ALM
Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) and Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) are topics related to advanced practices in systems and software engineering, and product management. They aim to improve efficiency, consistency and quality in the development, operation/service and maintenance of products and systems.

Interdisciplinary Consistency in Development and Service
Interdisciplinary consistency means that all aspects of development and maintenance of a product or system are seamlessly and consistently integrated across different specialist areas (such as mechanics, electronics and software) and phases in the lifecycle. This includes conception, design, implementation, testing, delivery and maintenance. The aim is to ensure that changes, requirements and information are efficiently mapped, referenced, synchronised and exchanged between the disciplines involved and across the entire product lifecycle. This avoids inconsistencies and improves product quality.
With consultancy, coaching and operational implementation, HOOD creates and improves the structural and technical conditions in development organisations that are necessary for interdisciplinary consistency at the level of working models, processes, methods and software tools. For this, we offer an range of services tailored to the customer’s situation:
- Discovery Workshop(s) for analysing engineering situations
- Establishing global configuration management with global traceability
- Developing and adapting working models, processes, methods and software tools for sustainable systems engineering
- Developing and adapting information models based on iterative/incremental and agile practices
- Anchoring efficient and effective management of product development and product service artefacts throughout the entire lifecycle
- Establishment of HOOD maturity models
Establishing Global Traceability
Traceability in this context refers to the ability to track the history, use or location of an element within a system across all stages of the lifecycle. Establishing global traceability requires implementing systems and processes that enable all elements of a product or system (such as requirements, design specifications, components and changes) to be tracked across different teams, locations and time zones. This is crucial for quality control, compliance and the efficient handling of changes and problems.


Establishing Global Configuration Management (CCVM)
Configuration management is a process for maintaining the consistency of a product or system, its functional and physical attributes, with its requirements, design and operational information throughout its lifecycle. Change and configuration verification and management (CCVM) is an extended form of configuration management that not only monitors the configuration, but also includes the verification and management of changes. Establishing global configuration management means establishing policies, procedures and tools to manage configurations and changes consistently across all locations and teams. This includes identifying configuration elements, controlling changes, recording and reporting configuration status and verifying compliance with requirements.
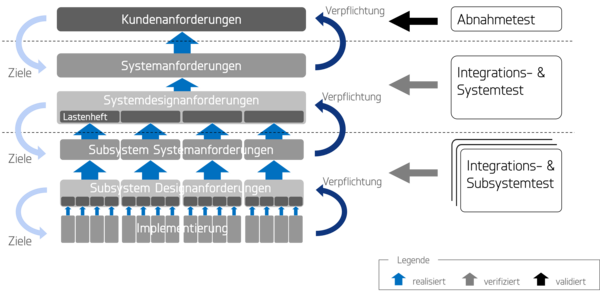
The HOOD Information Model
The information model developed by HOOD is a unique selling point from HOOD’s expertise in RE methodology. This conceptual information model lays the foundation for meeting the needs of modern, consistent systems engineering. Only by understanding the links between different requirements levels is it possible to sensibly consider the related issues of “language”, traceability and the separation of problem and solution spaces.

HOOD Sustainable Systems Engineering (SuSE)
HOOD SuSE turns those affected into participants. Manageable steps are taken based on the company’s strategic direction and goals, with a focus on experiential learning. During successive pilot projects, insights are gained into how systems engineering (SE) can be used effectively (processes, methods, tool reports, information architectures, etc.). SE therefore starts in small, manageable projects in which tangible benefits are generated immediately. In the definition phase, an initial company, division or product standard is developed based on findings from the pilot projects.
Anchoring defines the infrastructure required for the long-term establishment of SE and the necessary responsibilities for processes, operational aspects etc. A companywide rollout can then begin. In this service phase, institutionalisation of the projects with defined SE improvement iteration takes place, managed by the company itself. All responsibilities and SE standards are clear, agreed and implemented. The effort required for applying the new SE standards to new projects is minimal.
HOOD Competencies in RE & SE
What makes us unique is our knowledge and experience of more than 20 years in requirements management and engineering, as well as in systems engineering; and over 10 years in coaching and organisational change management. One of the reasons for HOOD’s success is its expertise in processes and methodologies in the field of requirements engineering, systems engineering and in change management consultancy/coaching. Process models used in development organisations, such as a V-model based on ASPICE, can then be aligned using the HOOD Information Model that also includes test management. We have expert knowledge of many relevant software tools used in systems engineering. In the requirements management field, these include Codebeamer, DOORS, DNG, Polarion, Jama, RE4J and Visure RM. In the area of modelling, these include Cameo, CATIA Magic, Enterprise Architect, Innovator or Matlab Simulink and MagicDraw. Other tools in the SE environment are Confluence, JIRA, STAGES, GIT, test tools, etc.

Talk to us about your goals.
From analysis to implementation, we have the right experience, practices and methods for you and your engineering and product management throughout the entire product lifecycle.
